The hemispherical_cluster function¶
A the hemispherical_cluster() takes one mandatory argument and 4 keyword arguments.
The first required argument is an ASE Atoms object. This object will be the base pattern used to create a cluster.
It is usually a primitive cell of a structure. The 4 keywords arguments describe the dimensions of the cluster and
the location of the emitter atom:
emitter_tag: is an integer which is the tag of the emitter atom
emitter_plane: is an integer to tell in which plane to put the emitter
diameter: is the diameter of the hemispherically shaped cluster (in angströms)
planes: is the total number of planes
Three simple example are shown in the figure 1 below. These are cut view in the (xOz) plane of the clusters. the clusters were created with those commands:
from msspec.utils import hemispherical_cluster
from ase.build import bulk
iron = bulk('Fe', cubic=True) # The base cell to be repeated to shape a cluster
# The cluster 1a, with an emitter on the surface
cluster1a = hemispherical_cluster(iron, diameter=25, emitter_plane=0)
# The cluster 1c, with an emitter in the second plane
cluster1b = hemispherical_cluster(iron, diameter=25, emitter_plane=1)
# The cluster 1c, with an emitter in the third plane and with just one plane below
# the emitter
cluster1c = hemispherical_cluster(iron, diameter=25, emitter_plane=2, planes=4)
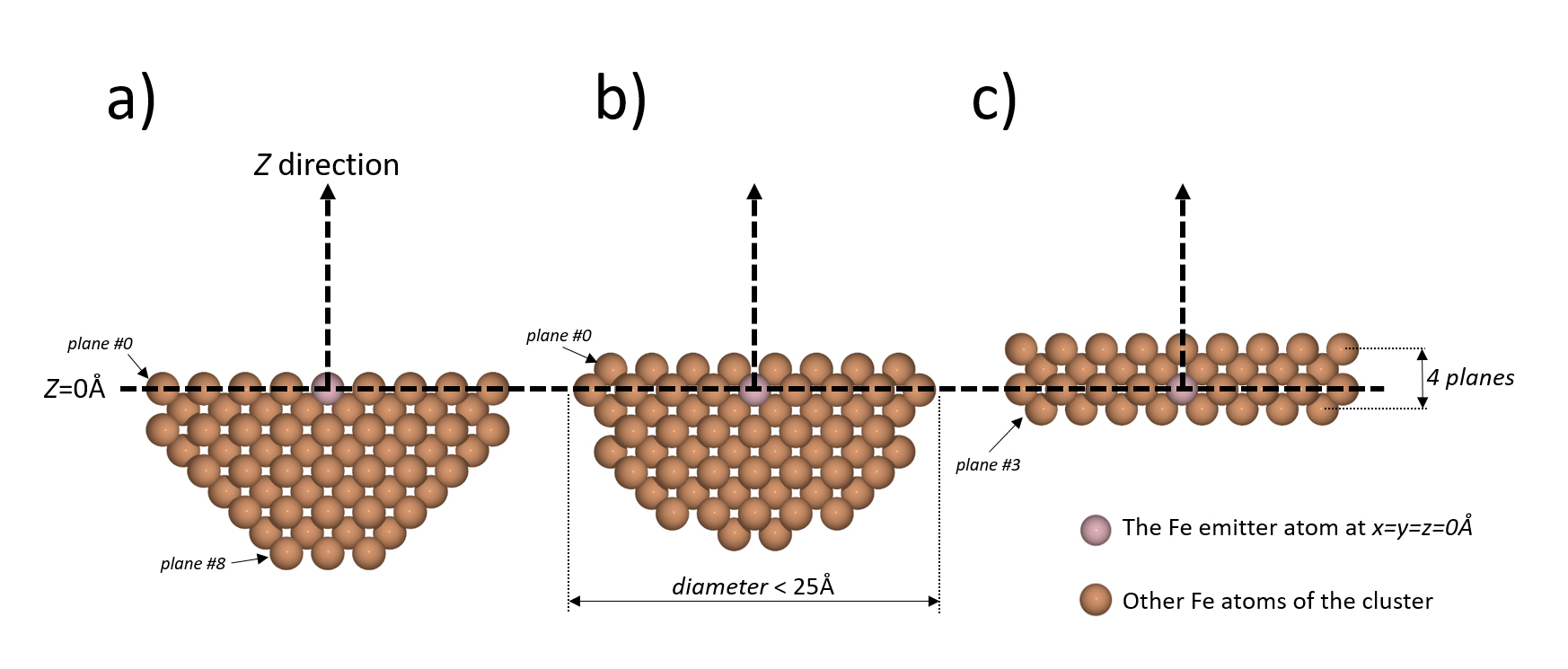
Figure 1.¶
The emitter_tag keyword is used to specify the emitter in a multielemental structure or if two atoms of the same kind exist in the primitive cell with different chemical or geometrical environment. For example, the CsCl structure is also bcc like the iron above, but the chlorine atom is at the center of a cube with 4 Caesium atoms on the apex. To get a Cl emitter in the desired plane, we should first tag it in the cell:
from msspec.utils import hemispherical_cluster
from ase.spacegroup import crystal
# Definition of this cubic cell
a0 = 2.05
a = b = c = a0
alpha = beta = gamma = 90
cellpar = [a, b, c, alpha, beta, gamma]
# Create the CsCl structure with the crystal function
CsCl = crystal(['Cs', 'Cl'], basis=[(0,0,0),(0.5,0.5,0.5)], spacegroup=221, cellpar=cellpar)
# by default, all atoms tags are 0
# set the Cl tag to 1
CsCl[1].tag = 1
# Create a cluster with the Cl emitter
cluster = hemispherical_cluster(CsCl, emitter_tag=1, emitter_plane=3, diameter=25)
The resulting cluster is shown in the figure 2 below
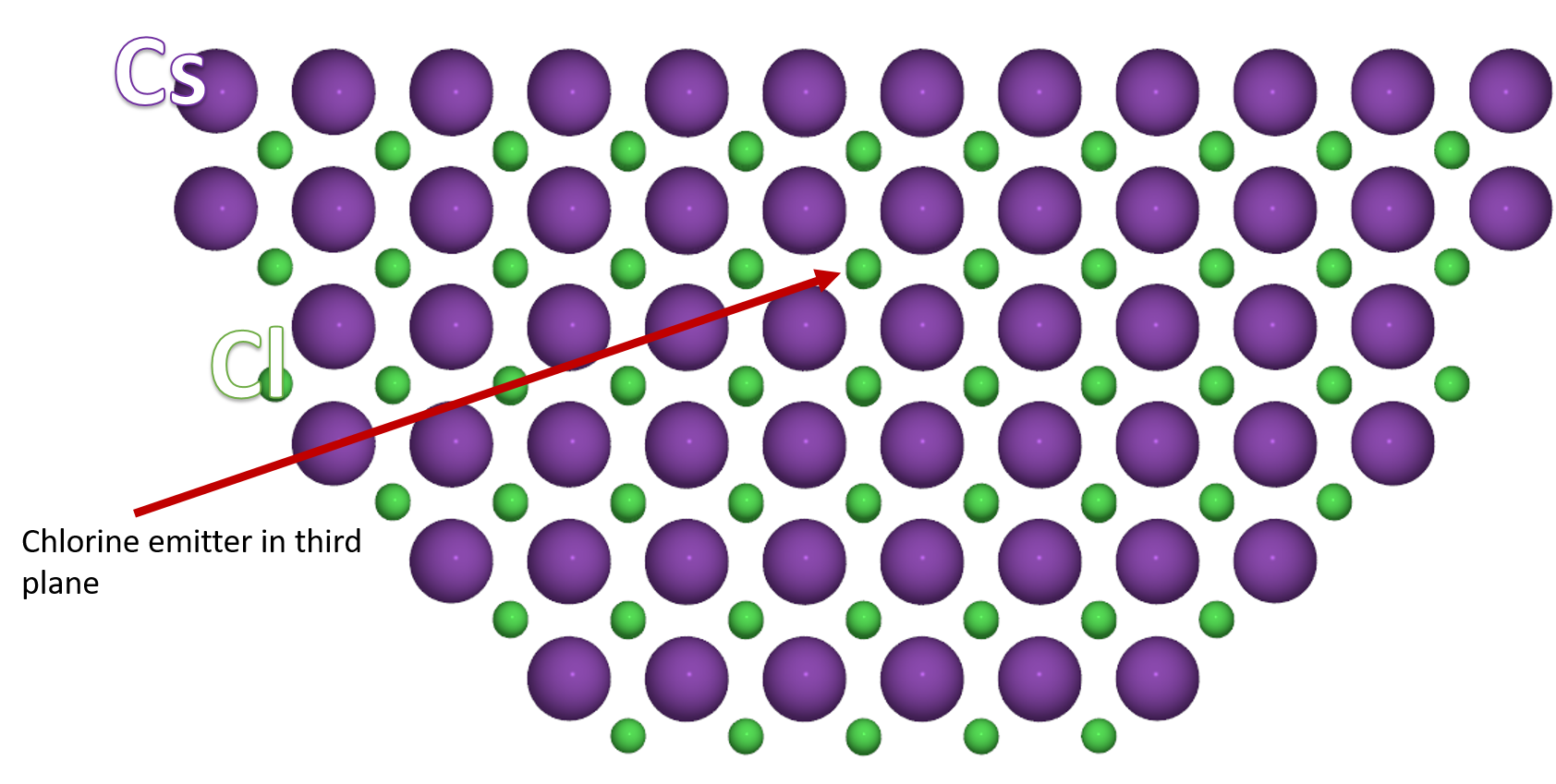
Figure 2. A cut view in the (xOz) plane of a CsCl cluster with a Cl emitter atom in the third plane¶